You follow the diet, count every calorie, skip your favorite meals and still, the weight swings back. The problem isn’t your effort, it’s the imbalance in how most diets work.
Your body needs more than restriction to stay healthy; it needs rhythm, variety, and nourishment. That’s where a balanced diet steps in, it feeds your body while still helping you lose fat the right way.
Think of it as the missing link between short-term diets and lifelong wellness, simple, sustainable, and actually doable.
What Is a Balanced Diet and Why is it Necessary for Overall health
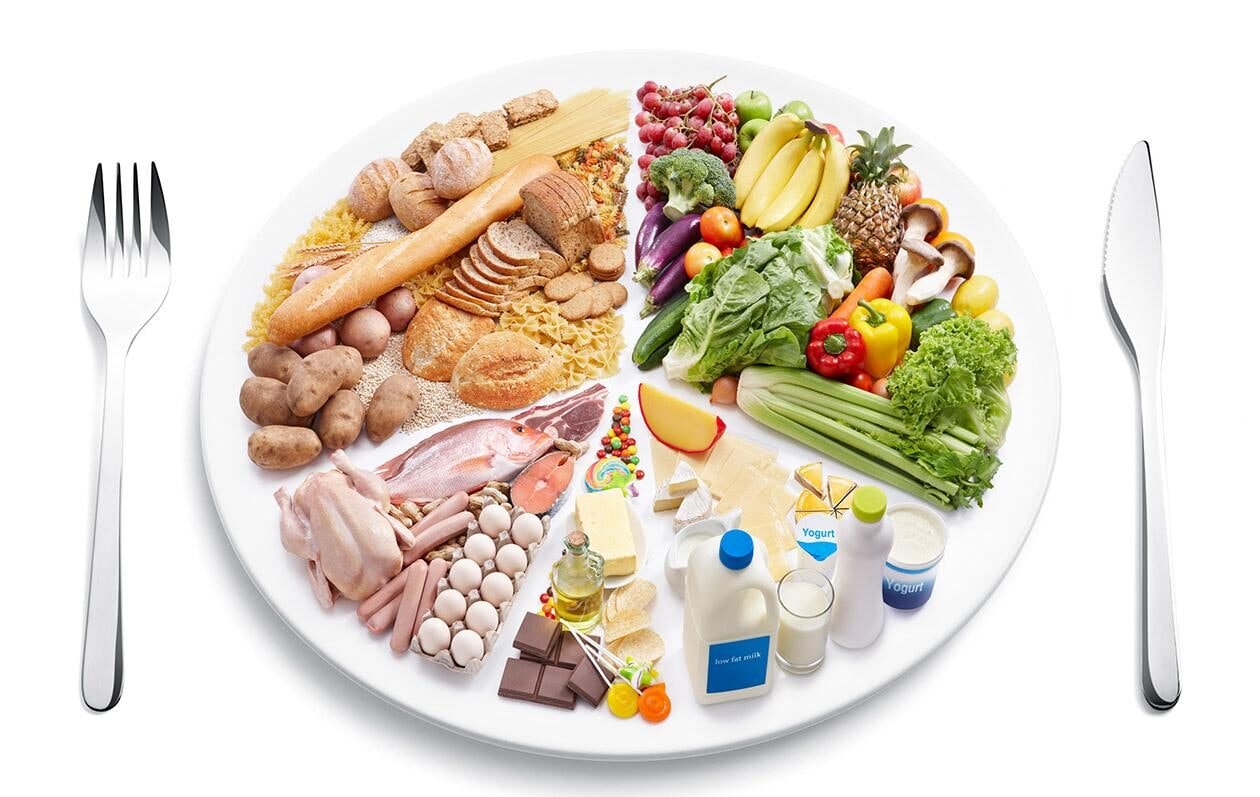

A balanced diet provides all the nutrients your body needs for good health, energy, and longevity. It supports optimal health, strengthens immunity, and maintains a healthy body through nutrient-rich foods that deliver essential nutrients for overall wellness.
At its core, a balanced diet supplies all six essential nutrients, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water, in the right proportion.
“Nutrition is not just about eating, it’s about learning to live.”
— Patricia Comptton, Registered Dietitian
Each one supports a different system: carbs fuel energy, proteins build muscle, fats protect cells, vitamins and minerals repair and regulate, and water keeps everything moving.
Key pillars of a balanced diet
-
Variety in meals: Mix colors, textures, and food groups, vegetables, fruits, grains, proteins, and dairy or alternatives.
-
Portion control: Eat according to your body’s hunger, not the plate size.
-
Quality over quantity: Choose natural, minimally processed foods rich in fiber and nutrients.
-
Hydration: Water is the body’s silent nutrient; it aids digestion and prevents fatigue.
How it benefits your body
-
Keeps blood sugar steady and boosts energy throughout the day.
-
Supports a healthy weight and improves digestion.
-
Strengthens the immune system and lowers disease risk.
-
Promotes clear skin, sharper focus, and better sleep.
Example:
Start your day with oats, milk or yogurt, a banana, and a sprinkle of nuts. This single bowl combines slow carbs, healthy fats, and protein, exactly what your body needs to stay fueled and alert.
A truly balanced diet isn’t a one-time fix; it’s a lifestyle rhythm that builds resilience from within. Up next, let’s break down how each food group contributes to this balance and where to find it in everyday meals.
Understanding Different Food Groups in a Balanced Diet
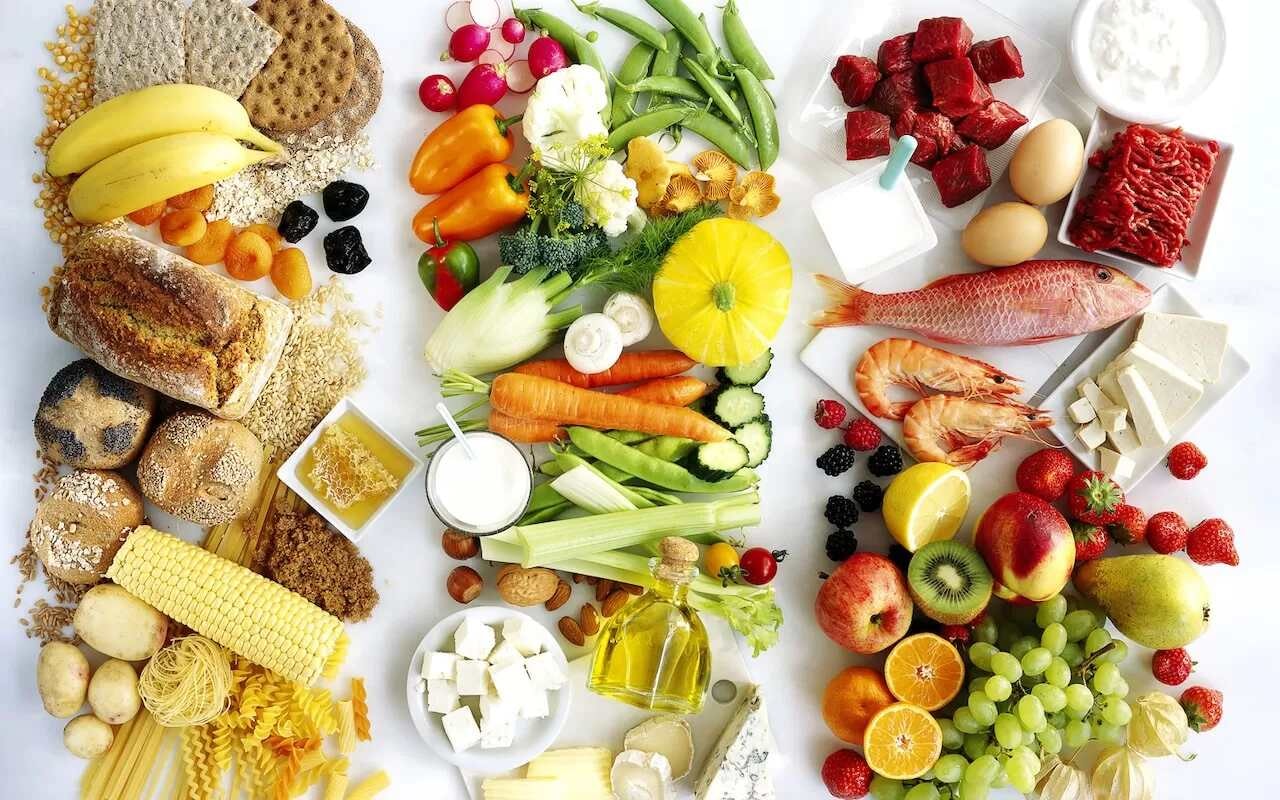

Each food group plays a unique role in building a strong and healthy body. From fruit and vegetables rich in vitamins to whole grains packed with energy and dairy foods that support calcium strength, every category adds its own health benefits.
“Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food.”
— Hippocrates
Let’s explore how these essential food groups work together for complete nourishment.
1. Fruits and Vegetables – Vitamins and Fiber
Fruits and vegetables deliver essential vitamins like vitamin C and minerals that support wound healing, better energy levels, and tooth health.
Adding fresh fruit, leafy greens, and sweet potatoes helps regulate cholesterol levels and keeps your diet rich in plant-based foods that promote daily vitality and long-term health.
They are the body’s natural detoxifiers, improving gut health and enhancing hydration. Regular intake also supports hormone regulation and stabilizes blood pressure, creating the foundation for disease prevention.
Example:
Start your day with papaya or berries and include a mixed vegetable curry for lunch to keep digestion smooth and energy steady.
2. Grains and Cereals – Energy and Nutrients
Whole grains such as brown rice, whole wheat pasta, and chia seeds are nutrient powerhouses that provide steady energy levels and help maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
They contribute complex carbohydrates that fuel physical and mental performance throughout the day. The fiber content also feeds beneficial gut bacteria, improving immunity and metabolism.
Example:
Have oatmeal for breakfast or switch from white bread to whole wheat rotis for lunch to sustain energy without afternoon fatigue.
3. Protein-Rich Foods – Growth and Repair
Protein-rich foods like grilled fish, chicken curry, and other lean sources build muscle strength and repair tissues efficiently. Pairing them with plant-based foods ensures all essential amino acids are met for a balanced, nutrient-dense meal that keeps your body’s health goals firmly on track.
Protein also supports enzyme and hormone production, improving recovery and concentration. Distributing protein across meals helps maintain satiety and prevent late-night snacking.
Example:
Include sprouts or paneer in breakfast and grilled chicken or tofu at dinner to maintain muscle health and fullness.
4. Dairy Foods and Alternatives – Calcium and Strength
Dairy foods and dairy alternatives such as full-fat dairy products or low-fat diet options offer calcium, vitamin D, and protein vital for bone and muscle health. Smart choices like choosing foods with clean food labels and moderate fat intake contribute to a healthier, more balanced plate.
Beyond bone health, dairy also supports nerve function and cell repair. Fortified non-dairy options like soy or oat milk ensure similar nutrient benefits for those with lactose intolerance.
Example:
Add yogurt to your lunch or drink a glass of fortified soy milk in the evening for consistent calcium intake.
5. Fats and Oils – Energy and Hormone Balance
Healthy fats from olive oil, coconut oil, and vegetable oils stabilize hormone levels and support nutrient absorption. Avoid trans fats or visible fat from fried foods and packaged foods that can harm heart health. Prioritizing unsaturated fats maintains good cholesterol balance and fuels long-term energy.
These fats also act as carriers for vitamins A, D, E, and K and improve brain function. A small portion daily keeps you satisfied and maintains healthy skin and metabolism.
Example:
Add a teaspoon of olive oil to salads or snack on walnuts for brain and heart-friendly fats.
6. Sugars and Discretionary Foods – Occasional Treats
Processed meats, sugar-sweetened beverages, and drinks high in free sugars can quickly undo a balanced diet’s progress.
Keeping such foods as rare indulgences helps prevent insulin spikes and unnecessary cravings. Even natural sweeteners should be portioned wisely to maintain metabolic balance.
Example:
If you crave sweetness, try fruit juice or jaggery in moderation instead of refined desserts.
Each group adds a vital layer to your diet’s overall balance. Next, you’ll see how combining them smartly multiplies their nutritional impact and helps your body absorb more from every meal.
Food Group Combinations for Better Nutrition
Combining nutrient-dense foods the right way helps your body absorb all the essential nutrients efficiently. Pairing fresh fruit with healthy foods or balancing grains with proteins ensures optimal nutrient absorption and improved health benefits.
“The magic happens not in the ingredients alone, but in how you combine them.”
— Dr. Mark Hyman, Functional Medicine Expert
These combinations reveal how simple, balanced meals can power better energy and long-term vitality.
1. Combining Grains with Legumes for Complete Protein
Grains are low in lysine and legumes are low in methionine. Together, they create complete protein and steady energy, which supports muscle recovery and reduces risk of weight gain from excess snacking.
• Builds a more balanced amino acid profile
• Stabilizes blood sugar and keeps you full longer
• Supports active lifestyles and consistent physical activity
Example:
Brown rice with rajma or whole wheat roti with chana masala forms a classic high-protein, low-fat combination that fits easily on a healthy plate.
2. Pairing Fruits with Nuts for Sustained Energy
Fruit gives quick glucose while nuts add fat and protein to sustain energy release. This helps prevent mid-day fatigue and supports better concentration for work or study.
• Balances natural sugars with good fats
• Reduces the risk of tooth decay from excess sugar exposure
• Keeps metabolism steady through small, smart snacks
Example:
An apple with ten almonds or banana slices over peanut butter toast keeps energy consistent without more calories.
3. Mixing Vegetables with Healthy Fats for Nutrient Absorption
Healthy fats boost absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K in vegetables. This combination supports hormone balance, heart function, and reduces inflammation that contributes to developing heart disease.
• Improves nutrient absorption
• Enhances taste without extra salt or sugar
• Encourages long-term cardiovascular strength
Example:
Toss steamed spinach and carrots with olive oil and lemon, or top stir-fried veggies with crushed peanuts.
4. Adding Dairy Foods to Meals for Calcium Boost
Dairy or fortified alternatives add calcium, vitamin D, and protein that strengthen bones, teeth, and muscles. Including them with meals makes absorption more effective and supports public health goals of reducing nutrient deficiencies.
• Strengthens bones and prevents tooth decay
• Improves metabolism and bone density
• Aids better muscle recovery after physical activity
Example:
Add a cup of curd with lunch or drink fortified soy milk alongside your evening meal for a calcium-rich boost.
5. Balancing Protein and Carbohydrates for Stable Blood Sugar
Pairing lean protein with complex carbohydrates maintains steady glucose and energy levels, preventing crashes that lead to cravings. It’s a simple, science-backed step toward better weight control and sustained performance.
• Keeps blood sugar balanced throughout the day
• Reduces risk of overeating and unnecessary weight gain
• Boosts recovery and strength for regular physical activity
Example:
Grilled fish with quinoa or paneer bhurji with whole wheat rotis gives stable energy without excess fat.
6. Including Fiber-Rich Foods with Every Meal
Fiber improves gut health, cholesterol balance, and fullness. It’s a natural appetite regulator that prevents sudden hunger spikes and long-term risks like developing heart disease.
• Enhances digestion and detoxification
• Supports heart and cholesterol health
• Maintains fullness between meals
Example:
Add chia seeds to breakfast oats or include sprouts and salads in lunch to improve digestion and balance calorie intake.
7. Using Herbs and Spices to Enhance Digestion and Flavor
Herbs and spices make food satisfying without excess oil or sugar. They add antioxidants, support digestion, and reduce reliance on processed condiments that often contain hidden calories.
• Promote better gut function and metabolism
• Reduce sodium dependence
• Keep meals flavorful while supporting overall health
Example:
Season vegetables with turmeric, cumin, and coriander, then garnish with mint or basil to boost both aroma and digestion.
Each combination turns your daily meals into functional nutrition that supports long-term wellness. Up next, you’ll see how a sample balanced diet plan brings these pairings together for real-world results.
Sample Balanced Diet Plan to Lose Weight and Stay Healthy
A sample balanced diet chart focuses on nutrient-rich meals that promote a healthy body weight and steady energy. It includes whole grains, lean proteins, and fresh fruit to help you lose weight naturally without restriction.
Exploring this plan shows how balanced meals can make everyday eating simple and effective for sustainable wellness.
| Day | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | Snacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Oatmeal with milk, chia seeds, sliced apple | Brown rice with lentil curry, cucumber salad | Grilled fish or tofu with steamed broccoli | Handful of almonds or green tea |
| Tuesday | Vegetable poha with peanuts, lemon | Quinoa chickpea salad with olive oil, cucumber | Paneer stir-fry with brown rice and spinach | Low-fat yogurt with fresh fruit |
| Wednesday | Smoothie with banana, oats, skim milk | Whole wheat roti with dal and sautéed vegetables | Baked chicken or soy chunks with salad | Papaya or pomegranate bowl |
| Thursday | Boiled eggs with whole grain toast, tomatoes | Vegetable pulao with curd, mint chutney | Baked fish or tofu with lemon dressing | Roasted chickpeas |
| Friday | Upma with vegetables, coconut chutney | Whole wheat wrap with grilled chicken or paneer, salad | Mixed vegetable curry with brown rice | Buttermilk or a small fruit bowl |
| Saturday | Overnight oats with almonds and berries | Lentil soup with quinoa and green salad | Grilled paneer with sautéed vegetables | Green smoothie or coconut water |
| Sunday | Whole wheat pancakes with fruit toppings | Vegetable khichdi with curd, papad | Baked tofu or fish with steamed vegetables | Nuts or herbal tea |
This 7-day plan keeps calories steady and nutrients balanced, so meals feel satisfying without being heavy. The mix of whole grains, lean proteins, vegetables, fruit, and healthy fats supports energy, curbs cravings, and protects long-term health.
Practice this pattern consistently, and your diet becomes a sustainable rhythm, not a short phase.
How a Balanced Diet Strengthens Immunity and Prevents Common Diseases
Eating a balanced mix of whole grains, olive oil, and healthy fat helps reduce heart disease, manage blood pressure, and prevent chronic diseases. By including fruit and vegetables, dairy foods, and nutrient-dense meals, you support immunity and improve long-term health.
This connection highlights how daily food choices directly protect your overall wellness.
1. Obesity – Controlled by balanced calorie intake
A balanced diet limits excess calorie intake while still providing energy for daily activities. Eating moderate portions of high-fiber and protein-rich foods helps control hunger and prevent unnecessary weight gain.
Example: Replacing fried snacks with roasted nuts or fruit keeps calories in check while still satisfying cravings.
2. Type 2 Diabetes – Managed through low-GI foods
Low glycemic index foods keep blood sugar levels stable and help your body respond better to insulin.
-
Lentils, oats, and brown rice release energy gradually throughout the day.
-
Regular intake of low-GI meals prevents sugar crashes and supports metabolic balance.
3. High Blood Pressure – Reduced by low-sodium meals
Reducing salt and adding natural potassium-rich foods keeps blood pressure in a healthy range.
-
Fresh fruits, vegetables, and unsalted nuts help maintain electrolyte balance.
-
Avoiding processed snacks and packaged sauces limits hidden sodium intake.
4. Heart Disease – Prevented with healthy fats
Healthy fats from olive oil, nuts, and fish raise good cholesterol and protect arteries. Avoiding trans fats lowers inflammation and prevents plaque buildup that contributes to developing heart disease.
5. Anemia – Avoided with iron-rich foods
Iron improves oxygen transport and prevents fatigue caused by low hemoglobin.
-
Sources include spinach, eggs, lentils, and lean meats.
-
Adding vitamin C–rich fruits like oranges or guava helps your body absorb iron better.
6. Osteoporosis – Prevented by calcium and vitamin D
Strong bones depend on steady calcium intake and enough sunlight for vitamin D synthesis.
-
Dairy, tofu, leafy greens, and fortified foods support bone density.
-
Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium effectively and reduces bone loss over time.
7. Digestive Disorders – Improved by high-fiber diet
Fiber from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables promotes smooth digestion and reduces constipation. It also feeds good gut bacteria, improving nutrient absorption and immune strength naturally.
8. Weak Immunity – Boosted by vitamins and minerals
Micronutrients strengthen your body’s defense system and improve recovery from illness.
-
Vitamin C, zinc, and omega-3s increase white blood cell activity.
-
Antioxidants from fruits, herbs, and spices reduce inflammation and cell damage.
Every nutrient in your diet plays a defensive role, keeping your organs strong and immunity active. But while good nutrition protects your health, small everyday mistakes can quietly undo those benefits.
Understanding what to avoid is just as important as knowing what to eat and that’s where the next section begins.
Your immunity starts in the kitchen. Discover doctor-approved recipes and nutrition insights at Balance Bite
Common Mistakes to Avoid in a Balanced Diet
Skipping meals, consuming processed foods, or eating too much saturated fat often disrupts good nutrition. Avoiding trans fats, free sugars, and fried foods while maintaining mindful eating habits supports a healthier life.
These mistakes are easy to fix once you understand how small dietary changes shape long-term wellness and energy.
1. Skipping Entire Food Groups
Avoiding whole food groups robs your body of key nutrients and weakens energy balance. A balanced plate should always include a mix of proteins, carbs, and fats in moderate portions.
Example: Cutting out dairy completely can reduce calcium and vitamin D intake, leading to fatigue and weaker bones over time.
2. Relying Too Much on Processed Foods
Processed snacks often hide trans fats, refined sugar, and sodium that raise cholesterol and blood pressure. These foods add empty calories with little nutrition.
-
Choose fiber-rich, plant-based alternatives such as fruits, nuts, and homemade snacks.
-
Check labels for additives or hydrogenated oils before buying.
Example: Swapping packaged chips for roasted chickpeas adds fiber and protein without the junk calories.
3. Ignoring Portion Control
Even nutrient-dense meals can cause weight gain when portions grow unnoticed. Smaller plates, mindful eating, and slow chewing help your brain register fullness faster.
Example: Two tablespoons of peanut butter are healthy, but half a jar adds hundreds of hidden calories.
4. Consuming Too Much Sugar or Salt
Sugary drinks, fried foods, and processed meats overload your system with refined carbs and sodium, increasing blood pressure and risk of developing heart disease.
-
Replace soft drinks with fruit-infused water.
-
Limit salty sauces and snacks to once or twice a week.
Example: A single can of soda can exceed your entire day’s recommended sugar intake.
5. Not Eating Enough Fruits and Vegetables
Fresh fruits and vegetables supply vitamins, minerals, and fiber that keep your body strong and prevent chronic disease. Aim for color variety on your plate to cover all nutrient needs.
Example: Adding spinach, tomatoes, and bell peppers to one meal daily can drastically boost vitamin C and iron intake.
6. Cutting Out Healthy Fats Completely
Your body needs unsaturated fats for hormone balance, vitamin absorption, and steady energy. Eliminating all oils or nuts often leads to dry skin, fatigue, and poor focus.
Example: A drizzle of olive oil or a handful of almonds adds essential fatty acids without excess calories.
7. Following Fad Diets Without Guidance
Trendy diets that remove key nutrients or promote extreme calorie cuts may lead to nutrient deficiencies and rebound weight gain. Sustainable eating always wins over shortcuts.
Example: A no-carb diet might shrink your weight fast, but it also drains energy and triggers cravings later.
Mistakes in eating aren’t signs of failure, they’re signals to adjust.
Recognizing and correcting these patterns early helps you maintain balance naturally and prepares you for the next step: learning how to sustain a healthy diet for life.
Tips to Maintain a Balanced Diet for Lifelong Health

Maintaining portion control, choosing healthy eating habits, and building balanced meals every day lead to optimal health and a healthier life. Consistency with nutrient-rich foods creates a sustainable rhythm that keeps your body strong and energized.
These principles show how everyday routines can evolve into a lifelong practice of good health.
1. Build Consistent Eating Habits Every Day
Consistency shapes metabolism. Eating at similar times daily helps your body anticipate hunger and digestion better, improving nutrient absorption and preventing random snacking.
Example: Have breakfast within one hour of waking and dinner two to three hours before sleep for better energy balance.
2. Maintain Portion Control Without Overthinking
You don’t need to count every calorie to eat mindfully. Using smaller plates and eating slowly trains your body to recognize fullness naturally.
-
Divide your plate into half vegetables, one-quarter protein, and one-quarter whole grains.
-
Avoid second helpings until you’ve waited ten minutes after finishing.
Example: A cup of rice and a palm-sized portion of protein keep your meal balanced and satisfying.
3. Include Variety from All Food Groups
No single food provides everything your body needs. Rotate between cereals, legumes, vegetables, fruits, and proteins to cover all essential nutrients and avoid monotony.
Example: Alternate between chickpeas, lentils, and beans through the week for protein diversity.
4. Plan and Prep Meals Ahead of Time
Planning reduces last-minute unhealthy choices and helps maintain a balanced intake through busy days. Batch-cook or pre-chop ingredients so healthy meals are always within reach.
Example: Keep boiled eggs, cut fruit, or pre-cooked grains ready in the fridge for quick meals.
5. Balance Indulgence with Discipline
A lifelong healthy diet doesn’t ban treats, it manages them wisely. Enjoy your favorite foods occasionally without guilt, but balance them with nutrient-rich meals the rest of the day.
Example: If you eat dessert after dinner, balance it by skipping added sugar drinks that day.
6. Stay Active to Support Your Diet Goals
Physical activity works hand in hand with diet to maintain healthy body weight and metabolism. Regular movement helps use the energy you eat, keeping fat levels under control.
-
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate activity weekly.
-
Include stretching or strength training for better flexibility and tone.
7. Monitor Progress and Make Small Adjustments
Track your meals, weight, and energy levels periodically. Adjust portions, add variety, or swap ingredients if you notice fatigue or weight changes. Small shifts prevent big imbalances.
Example: If you feel sluggish after meals, reduce refined carbs and add fiber instead.
8. Prioritize Hydration and Mindful Eating
Dehydration can mimic hunger, leading to unnecessary snacking. Drinking water before meals and chewing slowly promotes better digestion and focus during eating.
Example: Drink a glass of water 15 minutes before meals to curb overeating naturally.
Healthy eating isn’t a challenge, it’s a rhythm you build with time.
When balanced choices become second nature, food stops being a struggle and turns into your biggest long-term ally for sustained energy and health.
Consistency begins with one good choice. Let Balance Bite guide your next meal toward lasting balance and better energy
FAQs
1. How Does Healthy Eating Differ From a Regular Diet?
Healthy eating focuses on long-term balance and nourishment, while regular diets usually aim for short-term restriction or weight loss.
2. What Are the Key Components of a Healthy Diet Plan?
A balanced mix of whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, fruits, vegetables, and proper hydration in controlled portions.
3. How Can Portion Control Help Maintain Long-Term Wellness?
It prevents overeating, keeps calorie intake aligned with energy needs, and supports stable weight and metabolism over time.
4. When You Need to Lose Weight, How Should You Adjust Your Balanced Diet?
Slightly reduce overall calorie intake, focus on high-fiber and protein-rich meals, and limit added sugars and refined carbs.
5. What Are Some Simple Everyday Habits to Make Healthy Eating Easier?
Plan meals ahead, keep nutritious snacks handy, drink plenty of water, and eat slowly without distractions.
6. Why Is a Balanced Diet Important for Mental Health and Focus?
It maintains steady blood sugar, fuels the brain with essential fats and vitamins, and helps reduce fatigue and mood swings.
Conclusion
A balanced diet plan only works when you act on it daily. Start by structuring your meals, tracking portions, and keeping variety on your plate. Small, consistent actions create big results over time.
If your goal is lasting health, make every meal a conscious choice, one that fuels your body, sharpens your energy, and keeps progress steady without forcing restriction.
Ready to eat smarter, not lesser? Explore science-backed diet plans crafted for real lifestyles on Balance Bite




















Leave a comment
Translation missing: en.blogs.comments.discription